Thermal imaging technology enhances battery quality during manufacturing by identifying material discrepancies and thickness variations in battery electrodes. This ensures that only high-quality electrodes are used, improving battery performance and safety.
 Thermal Imaging Technology in Lithium-ion Battery Manufacturing
Thermal Imaging Technology in Lithium-ion Battery Manufacturing

Q&A with David C Bursell | MoviTHERM
How is Thermal Imaging Impacting the Li-Ion Battery manufacturing, usage, and disposal?
From manufacturing to usage and eventual disposal, lithium-ion batteries are integral components in various technologies. Thermal imaging plays a critical role in ensuring the safety and quality of lithium-ion batteries at every stage of their lifecycle.
Ensuring Manufacturing Quality with NDT
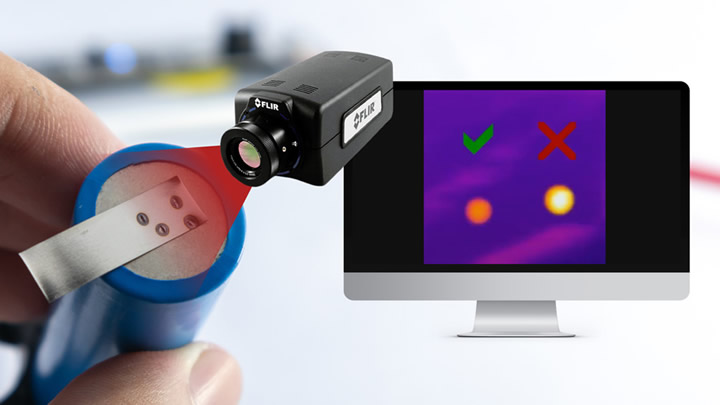
Contaminant Detection in Electrodes
The quality of a lithium-ion battery often starts with its electrodes. Thermal imaging can detect material composition and thickness discrepancies, helping identify contaminants or inconsistencies. Such precision ensures that only high-quality electrodes are used, enhancing the battery's performance and safety.
Weld Quality Assurance
Welding the components of a battery needs to be executed with extreme precision, as a faulty weld can lead to safety hazards. Thermal imaging can assess the quality of these welds in real-time by detecting inconsistent temperature patterns that may indicate a poor-quality weld.

Monitoring for Safe Storage, Transport, and Usage
Fire Prevention during Storage and Transport
Lithium-ion batteries can be volatile and risk catching fire under certain conditions. Thermal imaging technology can continuously monitor the temperature of batteries during storage and transport, enabling timely intervention if abnormal heat patterns are detected.
Preventing Thermal Runaway during Charging and Usage
The thermal runaway phenomenon—where a rise in temperature leads to conditions that further increase the temperature—is a critical safety concern with lithium-ion batteries. Thermal imaging can actively monitor the battery temperature during charging and usage, allowing for quick action if signs of thermal runaway are detected.
Safeguarding the Waste Stream
Fire Prevention in Waste and Recycling Centers
Discarded lithium-ion batteries pose a fire risk when they end up in waste and recycling centers. Thermal imaging cameras can monitor these facilities to detect hot spots where a fire could erupt, allowing for preventive measures to be taken before an incident occurs.
 In what ways does thermal imaging assist in ensuring the quality of welds in lithium-ion batteries, and why is this crucial for safety?
In what ways does thermal imaging assist in ensuring the quality of welds in lithium-ion batteries, and why is this crucial for safety?
Thermal imaging assesses weld quality by detecting inconsistent temperature patterns on battery welds. Poor welds can lead to increased electrical resistance or shorts. Both defects compromise battery performance and could lead to an unsafe thermal runaway condition. Thermal imaging helps identify these defects and rectify any issues early.
How is thermal imaging keeping industries safe with early fire detection?
Prevention is the best policy in the industrial sector, where fire hazards could result in catastrophic damage. Thermal imaging is one of the most potent tools for early fire detection. This technology is now a cornerstone in maintaining the safety of facilities.
Detecting Hot Spots Before Smoke or Flame
In many industrial fires, the first indicators are hot spots—areas of excessive heat that can serve as a precursor to flames. Traditional smoke detectors and even flame detectors may not pick these up, especially if they are in areas that are not easily visible. Thermal imaging cameras can identify these hot spots long before they turn into smoke or fire, enabling quick intervention and thus preventing a possible disaster.
IoT-Enabled Situational Awareness
Fixed thermal imaging cameras can be integrated into a broader Internet of Things (IoT) system, including fire detection devices like smoke detectors and heat sensors. This integration provides a more comprehensive situational awareness of the facility’s fire safety. When one sensor picks up a potential risk, other sensors can double-check, reducing false alarms and allowing for a more targeted emergency response.
Cloud-Based Alerting Systems
The real power of thermal imaging in fire detection comes into play when paired with cloud-based software. This software can analyze the data from thermal imaging cameras in real-time. If a potential fire is detected, it can immediately alert the necessary personnel through email, text, or even voice calls. This quick and targeted alert system enables immediate action, crucial for human safety and property damage mitigation.
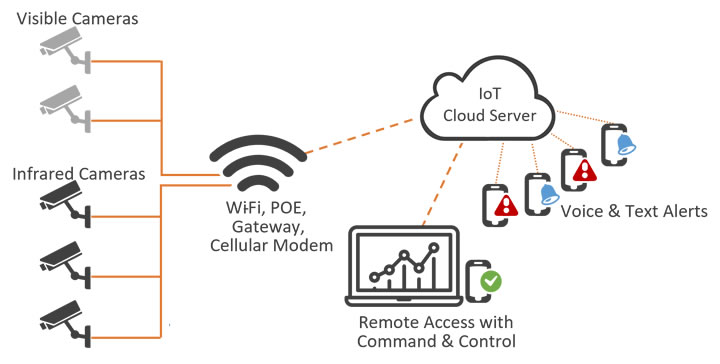
Can you explain how thermal imaging is used to prevent fire incidents during the storage and transportation of lithium-ion batteries? What are the benefits of this proactive approach?
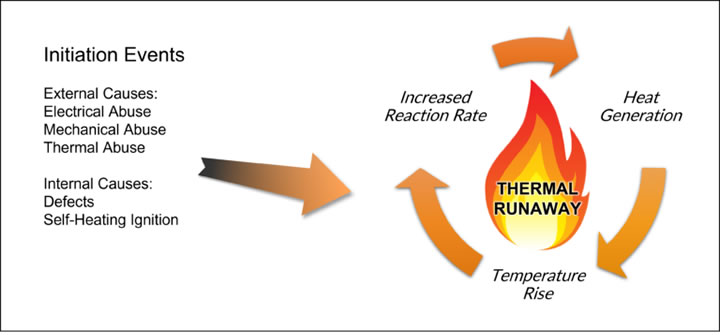
Thermal imaging can continuously monitor battery temperature during storage and transport. If abnormal heat patterns are detected, timely intervention can prevent the rapid spread of a fire caused by thermal runaway. The proactive approach prevents battery fire damage, loss, and safety risks.What is thermal runaway in lithium-ion batteries, and how does thermal imaging technology help monitor and prevent it during charging and usage?
Thermal runaway is a dangerous temperature escalation where a rise in temperature leads to conditions that further increase the temperature, ultimately resulting in a battery fire. Thermal imaging actively monitors battery temperature during charging and usage, allowing for quick action if signs of thermal runaway, such as rising temperatures, are detected. This helps prevent catastrophic battery failures and related safety risks.
About David C Bursell
David C Bursell is passionate about imaging technologies and solutions. For over 23 years, he has been extensively involved with infrared imaging science. He has worked for imaging companies, including Inframetrics, FLIR Systems, and MoviTHERM, where he is currently the Vice President of Business Development. His education includes a BS in Mechanical Engineering from Brigham Young University and an MBA from Boston University. He has also studied Digital Marketing Analytics at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. When not working with infrared cameras, David enjoys restoring old cars. A current project includes the restoration of a 1977 Toyota FJ40 Landcruiser.
The content & opinions in this article are the author’s and do not necessarily represent the views of ManufacturingTomorrow
Comments (0)
This post does not have any comments. Be the first to leave a comment below.
Featured Product

