The Manufacturing Talent Crunch and the CNC Machining Knowledge Capitalization
Manufacturers realize the CNC machining sector is particularly affected by a skills gap, leading to a shortage of qualified machinists. This gap can hinder the production of precision parts and components. In this article, George Chen, DELMIA Senior Offer Marketing and Business Development Manager, takes a closer look at how advanced manufacturing could hold the key to addressing the skills gap in manufacturing.
Advanced Manufacturing is grappling with the talent crunch
The manufacturing and Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining industries are facing a talent crisis characterized by a shortage of skilled workers. According to Deloitte, the talent deficit is projected to persist, with an estimated 2.1 million unfilled manufacturing jobs in the United States alone by 2030[1][2]. Industry 4.0 is rapidly revolutionizing the manufacturing industries, demanding workforce with advanced skill sets. The skills gap in manufacturing is a significant contributor to this workforce shortage. Globally it has already led to 10 million manufacturing jobs worldwide remaining unfilled, affecting the industry’s ability to meet demand and grow efficiently[3].

Image Courtesy Deloitte Consulting and the Manufacturing Institute
Addressing the CNC machining skills gap
Manufacturers realize the CNC machining sector is particularly affected by a skills gap, leading to a shortage of qualified machinists. This gap can hinder the production of precision parts and components. Over 92% of manufacturing decision-makers are actively hiring machine operators[4]. Operating and programming CNC machines require skilled labor, and this expertise is in short supply in certain regions. Some of the specific knowledge and skills require specialized training and work experience, such as the ability to use CAD software (Computer-Aided Design), CAM software (Computer-Aided Manufacturing), and create and generate machining programs, to name a few. The scarcity of CNC skills and qualified professionals with key skills has made it challenging for manufacturers to meet their production demands and adapt to new technologies [5].
How could industries battle this challenge?
The manufacturing businesses continue to explore ways to solve the problem. Generally, they fall into one of the following categories.
Competitive Compensation: Offer competitive wages and benefits to attract skilled machinists. This can include increased rates and performance-based incentives[6].
Improved Work-Life Balance: Enhance the work environment by promoting work-life balance. Providing flexible schedules and reasonable workloads can make your company more attractive to potential employees[7].
Education Partnerships: Partner with educational institutions to create awareness of CNC machining careers. This can help bridge the skills gap by nurturing future talent[8].
Perception Repair: Address misconceptions about manufacturing and CNC jobs. Promote the industry’s technological advancements and opportunities for career growth[9].
Diversity and Inclusion: Focus on diversity in your hiring practices. Broaden the talent pipeline by actively recruiting individuals from diverse backgrounds, genders, and age groups[10].
All of these long-term endeavours take time to see impact. Often, businesses need immediate solutions to alleviate the bottleneck brought about by a talent drought. A veteran machining programmer goes on retirement, without the remaining talents to fully fill the skill gap. Suddenly the business is faced with some serious production issues and are in need of CNC skills.
A nimble approach to capitalize on knowledge
What if, the veteran machining programmers can store their expert knowledge into standardized programs, which can be accessed, replicated or tweaked by the broader team. Meet NC Knowledge Manager (NPX), a powerful role under Machining portfolio created by Dassault Système’s DELMIA brand.
NC knowledge Manager lets users define machining operations on specific features on a given part with all details including tool paths, cutting tools, macros etc. which can then be stored for reuse. These Know-How are saved as manufacturing cells in the platform. They can be revised and lifecycle controlled based on any changes that may be required. NC Knowledge Manager is not restricted to standard CAD features. Users can define any machinable geometry on a given part and identify that feature as a template. For instance, power features coming from engineering can be templatized for machining. This helps improve to reduce programming time, increase the quality of the machined part, mitigate user errors, and shorten the time required to program a quality part.
Automatic Know-How capitalization generation
NC Knowledge Manager provides the ability to automatically generate know-how of machining operations defined on features. It can be saved in the platform for reuse by other users on the platform.
Standardization and Re-usable best practices
NC Knowledge Manager enables the standardization of machining operations. This helps in defining operations, time consumed in defining details on an operation and helps in sustaining the quality and repeatability of the good and tested parameter for the tool path.
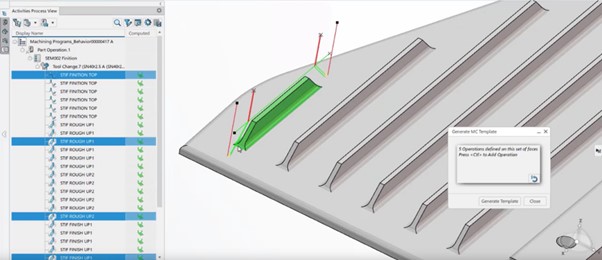
Increase productivity for NC Programmers by automating with NC Knowledge Manager
The usage of NC Knowledge Manager by all NC programmers will simplify the program creation and enable intelligent automatic NC process creation.
NC Knowledge Manager enables an NC Expert to capitalize on know-how and to share them through the Platform for re-use by the NC Programmers. An NC Expert knows what type of tool path, parameters, cutting conditions and macros are needed for specific feature materials or a given geometry to the machine (like pocket or stiffener). Once these different pieces of knowledge are saved and shared through the Platform. (thanks to a new “Machining Cell Know-How”) All the NC programmer needs to do to capitalize it, is search for the right knowledge, apply it to his current process, compute and the tool path is completed.
Customized NC knowledge Manager helps NC programmers to have a database of different and best practices usage of the companies and reduce potential errors for NC programmers in augmenting their productivity.
Create personalized activities
NC Knowledge Manager allows NC experts to customize all operation panels. They will have the capability to set the visibility, the sensitivity, the default value of parameter and the management of strategy tab like an administrator.
These customized operations are saved and shared through the Platform in Machining Cell to all the NC programmers. They will have a direct access to the customized operations in their workbench, like any default operation.
Comments (0)
This post does not have any comments. Be the first to leave a comment below.
Featured Product

