This article delves into the challenges posed by unreliable heat sealers and explores the solution of real-time thermal seal inspection systems to alleviate these concerns.
 Navigating the Frustration of Unreliable Heat Sealers in Automation
Navigating the Frustration of Unreliable Heat Sealers in Automation

Article from | MoviTHERM
The Importance of Reliable Heat Sealing in Automation
 One key component often responsible for sealing the deal (literally) in automated packaging processes is the heat sealer. However, despite advancements in technology, the frustration stemming from unreliable heat sealers remains a real concern for industries relying on flawless packaging.
One key component often responsible for sealing the deal (literally) in automated packaging processes is the heat sealer. However, despite advancements in technology, the frustration stemming from unreliable heat sealers remains a real concern for industries relying on flawless packaging.
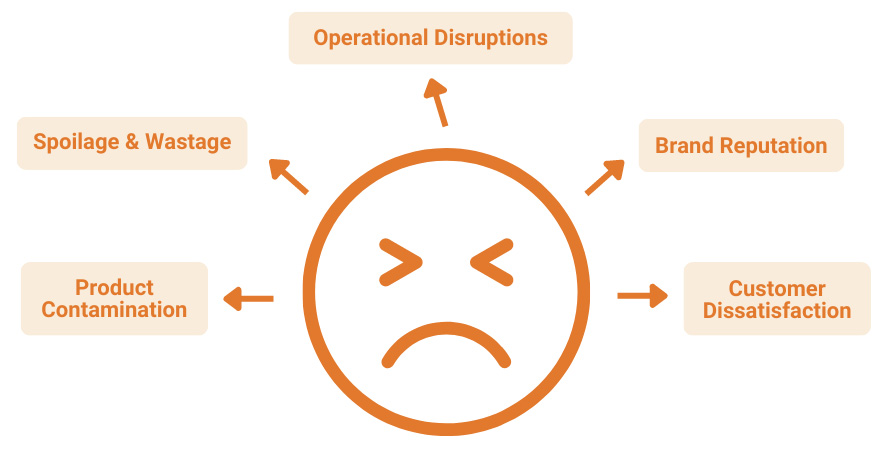
A reliable heat seal guarantees freshness, prevents contamination, and maintains the overall quality of the contents. Inconsistent or faulty seals can lead to costly consequences such as product spoilage, recalls, and reputational damage. This article delves into the challenges posed by unreliable heat sealers and explores the solution of real-time thermal seal inspection systems to alleviate these concerns.
The Frustration of Unreliable Heat Sealers
Unreliable heat sealers can lead to a cascade of issues. Operators may experience frequent interruptions in the production line due to resealing or rejecting improperly sealed packages. This not only hampers productivity but also increases operational costs.
Inconsistent seals can cause leakage, compromising the safety of products and potentially damaging brand trust. The frustration of dealing with these challenges highlights the need for a more dependable solution.
Types of Heat Sealer Technologies
Not all sealing machines are created equal, and understanding the different technologies available can shed light on the reliability spectrum. Here are the main types of heat sealer technologies:
Impulse Sealers
Suitable for low-volume applications, these sealers heat up only during the sealing process.
Continuous Sealers
Ideal for high-volume operations, these sealers maintain a constant level of heat.
Induction Sealers
Use electromagnetic fields for sealing without direct contact, making them suitable for heat-sensitive or tamper-evident packaging.
Each technology comes with its own set of benefits and challenges, impacting factors such as seal strength, consistency, and energy efficiency. However, even the most advanced heat sealer technology cannot eliminate the need for a robust inspection system to ensure the quality and reliability of seals in real-time.
How Heat Sealers Work
Heat sealers employ a combination of heat and pressure to fuse packaging materials, such as plastic films, creating a secure seal. This fusion is achieved by using heat to soften the materials at the sealing point and applying pressure to bond them together. However, factors like temperature inconsistencies, pressure variations, and material defects can lead to imperfect seals.
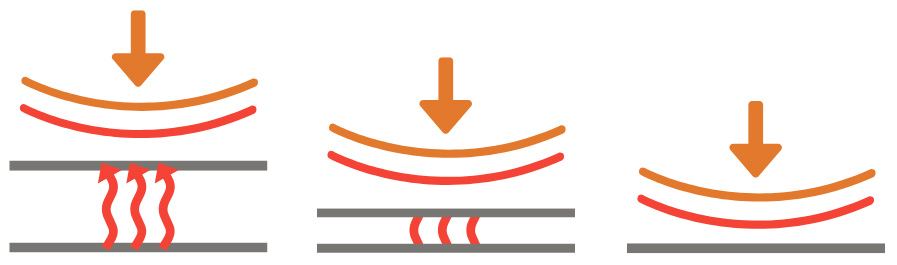
Common Causes of Heat Sealing Failures
While heat sealers are designed to create a secure bond between packaging materials, several common culprits can undermine their reliability.
Temperature Inconsistencies
Variations in machine settings or ambient temperature during the sealing process can result in imperfect seals.
Pressure Irregularities
Worn or improperly calibrated machinery can lead to incomplete or weak seals due to inconsistent pressure application.
Inadequate Sealing Materials
Low-quality films or laminates can compromise the overall integrity of the seal, leading to leaks or contamination.
Recognizing and addressing these root causes is crucial in the battle against unreliable heat sealing. However, even with diligent efforts to eliminate these issues, achieving consistently flawless seals may not always be guaranteed. This is where the integration of a reliable inspection system as part of your automation process line proves invaluable.
The Ultimate Solution to Detecting Faulty Seals
In the face of unreliable heat sealers, real-time thermal seal inspection systems emerge as a beacon of hope. These advanced inspection systems utilize infrared technology to detect defects in seals as they occur, ensuring that only properly sealed packages move forward in the production process. By using thermal imaging, these systems can identify temperature irregularities, seal breaches, and even foreign objects in the sealing area.
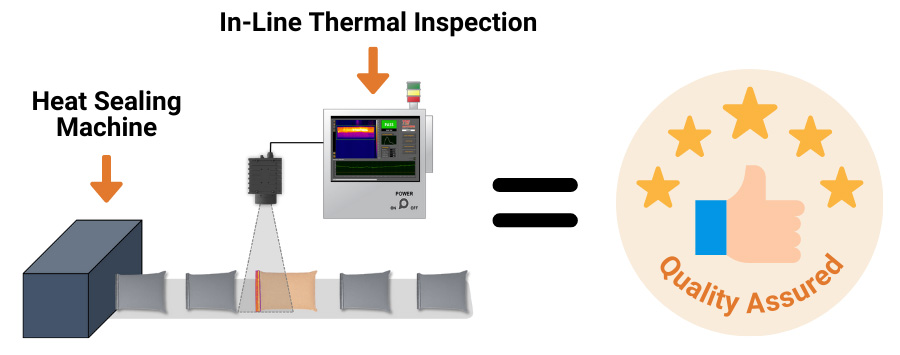
How Does Thermal Seal Inspection Work?
Thermal seal inspection systems rely on advanced thermal imaging cameras to capture and analyze the heat patterns of seals. When a seal passes through the inspection area, the system assesses its thermal signature against predetermined parameters. Deviations from these parameters trigger alerts, allowing operators to take immediate corrective action. This real-time intervention ensures that only properly sealed packages proceed down the production line.
Benefits of Implementing Thermal Imaging Into Your Process Line
Enhanced Quality Control
Real-time thermal seal inspection systems offer an additional layer of quality control, reducing the risk of defective seals escaping detection.
Increased Efficiency
With faulty seals identified immediately, production lines experience fewer interruptions, leading to improved operational efficiency.
Cost Savings
The costs associated with resealing, reworking, and potential recalls are significantly reduced, contributing to long-term cost savings.
Brand Protection
Ensuring consistently sealed packages bolsters brand reputation and consumer trust, vital in competitive markets.
Regulatory Compliance
Many industries are subject to strict packaging regulations. Real-time thermal seal inspection helps meet these requirements, avoiding non-compliance penalties.
Conclusion
The frustration stemming from unreliable heat sealers in automation is a genuine concern for industries that rely on consistent and secure packaging. However, the rise of real-time thermal seal inspection systems presents a viable solution to alleviate these frustrations.
By detecting defects in real-time, these systems not only enhance quality control and efficiency but also safeguard brand reputation and compliance. As technology advances, combining automation and real-time inspection will revolutionize the packaging industry, establishing higher benchmarks for dependability and efficiency.
The content & opinions in this article are the author’s and do not necessarily represent the views of ManufacturingTomorrow
Comments (0)
This post does not have any comments. Be the first to leave a comment below.
Featured Product

